
A current asset account which contains the amount of investments that can and will be sold in the near future. If the revenues earned are a main activity of the business, they are considered to be operating revenues. If the revenues come from a secondary activity, they are considered to be nonoperating revenues. For example, interest earned by a manufacturer on its investments is a nonoperating revenue. Interest earned by a bank is considered to be part of operating revenues. Sales are reported in the accounting period in which title to the merchandise was transferred from the seller to the buyer.
- On the other hand, when analyzing a manufacturing company, the efficiency ratios may tell us much more about the business.
- For such reason, valuation can be considered more of an art than a science.
- On the other hand, when the DPO is too high, it means a company delays paying its suppliers, which can lead to disputes.
- It should be clear that investors have to compare the ratio they calculate to the same ratio for other companies in the same industry, or to the industry average, to get an idea of what’s higher or lower.
Operating Profitability Ratio Analysis

For example, inventory turnover is crucial for retail, while debt-to-equity might be more critical for manufacturing. It’s essential to compare ratios within the same industry for accurate benchmarking. These ratios give you insights that raw numbers alone cannot, enabling you to spot trends, identify strengths and weaknesses, and make informed decisions. For example, the purchase or manufacturing of merchandise and the sale of the merchandise including marketing and administration. In the statement of cash flows the operating activities section identifies the cash flows involved with Insurance Accounting these activities by focusing on net income and the changes in the current assets and current liabilities.
Financial ratios are those numbers found in the statement of cash flows.
Since the gain is outside of the main activity of a business, it is reported as a nonoperating or other revenue on the company’s income statement. A distribution of part of a corporation’s past profits to its stockholders. A dividend is not an expense on the corporation’s income statement. Insurance Expense, Wages Expense, Advertising Expense, Interest Expense are expenses matched with the period of time in the heading of the income statement. Under the accrual basis of accounting, the matching is NOT based on the date that the expenses are paid.
#28 – Efficiency Ratio

Ratio analysis is usually rooted heavily with financial metrics, though ratio analysis can be performed with non-financial data. Key market prospect ratios petty cash include dividend yield, earnings per share, the price-to-earnings ratio, and the dividend payout ratio. Market prospect ratios help investors to predict how much they will earn from specific investments. The earnings can be in the form of higher stock value or future dividends.
Financial ratios can be used to compare companies as prospective investments. Moreover, they can provide a measure of a company today that can be compared to its historical data.The information you need to calculate ratios is easy to come by. Once you have the raw data, you can plug it into your financial analysis tools and put it to work for your benefit. Its calculation subtracts inventory from current assets before they’re divided by current liabilities. This ratio can present better insight into the short-term liquidity of the firm because of the exclusion of inventory.

Debt-to-Equity (D/E) Ratio
Solvency ratios, such as the Debt to Equity Ratio and Interest Coverage Ratio, are pivotal for small business owners. They help small businesses manage debt responsibly and signal financial health to potential investors. For instance, a boutique owner using the Debt to Equity Ratio can assess if they’re relying too much on borrowed funds versus their own investment to finance the store.
- A higher ratio shows that your business can comfortably cover its interest payments, a good sign of financial health.
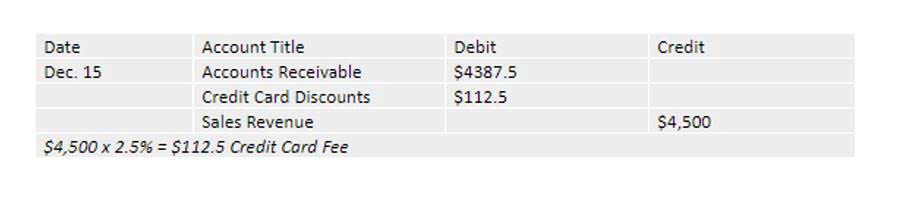
- Indeed, each time a customer buys goods, if the payment gets postponed at a later date, this event generates receivable on the balance sheet.
- This comparison will show how the company performs relative to itself and its competitors.
- Additionally, an investor can compare a ratio derived from certain data today to the same ratio derived from a long period of historical data.
- The published balance sheet of a corporation must also be comparative but requires only two columns of amounts (such as the amounts as of December 31, 2024 and the corresponding amounts for December 31, 2023).
- As the expenses are used or expire, expense is increased and prepaid expense is decreased.
How Ratio Analysis Works
Debt-to-assets and debt-to-equity are two ratios often used for a quick check of a company’s debt levels. They show how debt stacks up against the categories of assets and equity on the balance sheet. They give investors an idea of a company’s financial health as it relates to a potential burden of debt. A higher current ratio is favorable as it represents the number of times current assets can cover current liabilities. However, one that’s too high might indicate that a company isn’t utilizing its excess cash as well as it could to pursue growth. The debt-to-equity ratio how would you characterize financial ratios measures a company’s debt liability compared to shareholders’ equity.
- taniamos
- تیر 31, 1401
- 18 بازدید
